In this tutorial, we will cover how to set up and configure MySQL database inside Docker containers. We will go over concepts such as connecting to MySQL servers, running MySQL clients to connect to containers, and so on. Additionally, we will discuss how Stash can serve as an alternative solution in this context.
1. Create a project folder:
mkdir my-app
cd my-app
2. Create a docker-compose.yml file:
version: '3.8'
services:
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0 # Use the official MySQL 8 image
container_name: mysql8-container
ports:
- "3306:3306" # Map MySQL's default port to the host
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: mypass # Set the root password
MYSQL_DATABASE: mytestdb # Create a database
MYSQL_USER: myuser # Create a non-root user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: mypass # Set the password for the user
volumes:
- mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql # Persist MySQL data
networks:
- mysql-network
volumes:
mysql-data: # Named volume for persistent data
networks:
mysql-network: # Define a custom network
A docker-compose.yml file is a configuration file used by Docker Compose to define and manage multiple containers as part of a single application. It allows you to define services, networks, volumes, and other settings in a simple, declarative format.
3. Build the Docker image:
docker-compose build
4. Start the container:
docker-compose up -d
Verify the setup:
You can check if the container is running by using the command below:
docker ps
It lists all the running containers on your Docker system.
You can access the MySQL shell by running:
docker exec -it mysql8-container mysql -u myuser -p mytestdb
A quick way to set up a MySQL Docker container by using Stash
You can set up and configure a MySQL Docker container in a few steps without dealing with terminal commands, Dockerfile or docker-compose.yml.
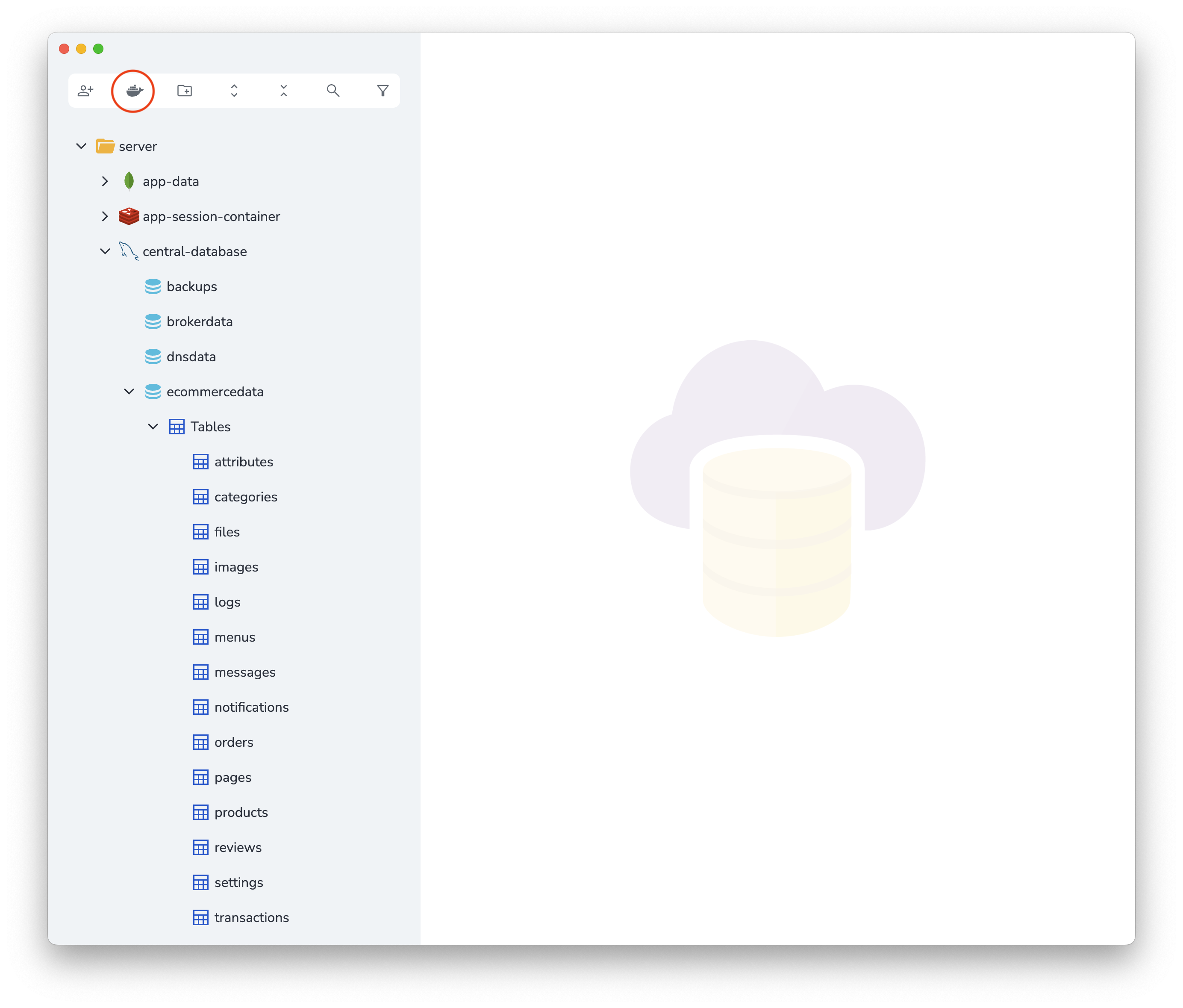
Open Stash app and click on the Docker icon on the sidebar.
Give your container a name and set a root password.
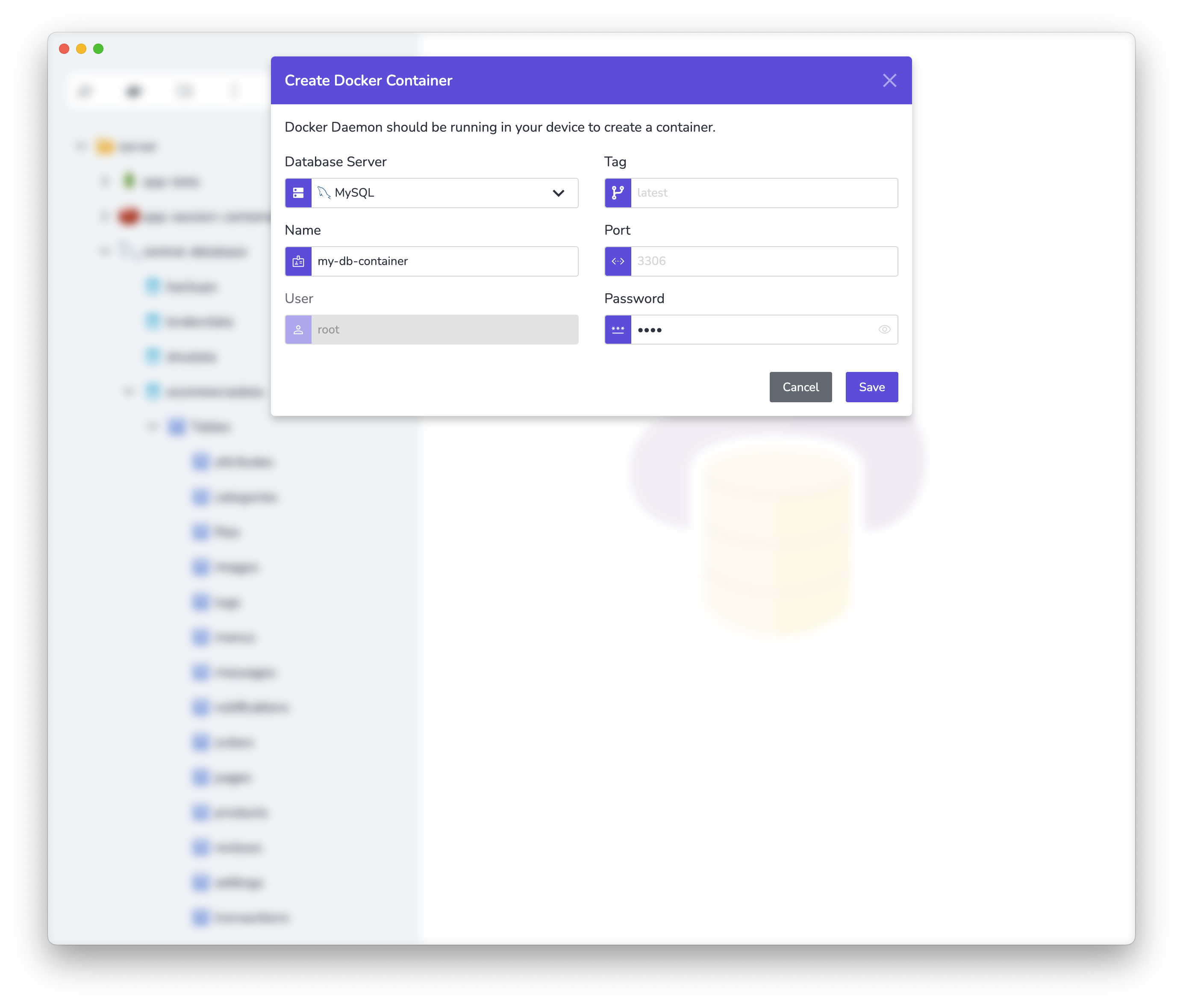
When you click the Save button, Stash will set up and configure a MySQL container in Docker.
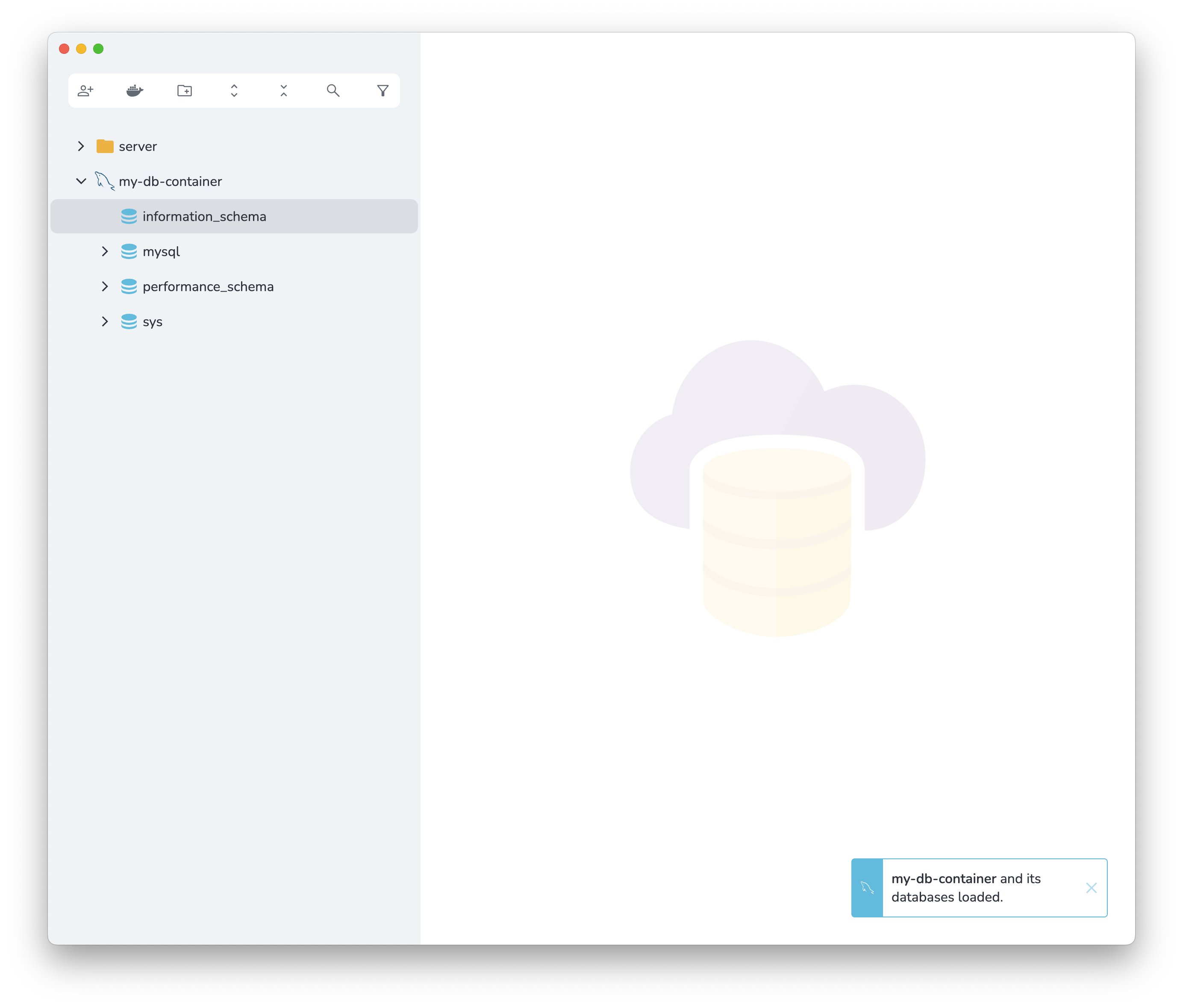
If you list the running Docker containers, you will see that Stash has created a container for you and set it up.
List the containers by running the command below:
docker ps
You should see a result similar to the following in the console.

That's it! Now, you can start working with your local MySQL server.